Machine learning, AI (artificial intelligence), and big data have been popular buzzwords over the last few years. Like it or not, their usage and usefulness will continue to increase year over year. As with any new product, service or concept, however, they come with pros and cons.
What is ChatGPT?
One of them, ChatGPT, an AI chatbot founded by OpenAI and released in November 2022, has commanded headlines for months now. While chatbots are often used by companies to help answer questions about services or provide customer support - something that saves them from employing humans to chat - ChatGPT is way more powerful. It can write blogs – not this one! – advertisements, or even code in seconds.
What’s the problem here? Services like ChatGPT or VirusTotal follow the same model: You’re the customer and supplier at the same time. While VirusTotal, an online service that analyzes suspicious files and URLs to detect malware, can let you check files for known malicious history or scan them, everything you upload is shared with dozens of anti-virus vendors and a community of tens of thousands of paid subscribers. ChatGPT is the same. There’s a human-created algorithm and tons of data behind the service.
ChatGPT's performance is heavily influenced by the amount and type of training data it has been exposed to. Whatever you give it, it saves for re-use in the future. While ChatGPT recently introduced the ability to turn off chat history, allowing you to choose which conversations can be used to train its models, it's not done by default, meaning the model is regularly trained on large amounts of text data.
Stories and articles about the dark side of ChatGPT have popped up in the news several times over the last few months, with headlines detailing employees allegedly leaking company secrets and source code to the chatbot, scenarios that could cost organizations untold sums of money.
Because the chatbot, and other large language models (LLMs) like Google Bard and Microsoft’s Bing, are so easy to use, it could put your own employees, whether they work remotely or at the office, contractors, and even parts of your supply chain at risk.
How does ChatGPT work?
Upon signing up, it asks you for your email, name, and phone number which means that questions and answers are attributed to a being, you.
When you first log in it shows a warning about sharing sensitive data, but but warnings and laws don't deter everyone.
Why does all of this matter from a data leakage point of view?
For one, ChatGPT could be used to exfiltrate work data on purpose and – once the employee – is at home extract what was pasted in on the work computer.
It could also lead to the accidental uploading of what the user may not realize is sensitive, like PCI (payment card data), PII (personal identifiable information), IP (intellectual property), or pricing lists. In either scenario, such inputs could be used by ChatGPT and displayed to future users or seen by human chat reviewers directly, jeopardizing the data.
How can my business keep our corporate secrets out of ChatGPT?
If you’re an organization, what are your options for controlling access to ChatGPT? Can you control what can be pasted into it?
When it comes down to it, ChatGPT is just like any other website with a text box and submit button. The service's chat function is like any other website that uses TLS (the secure padlock), and below you can see the service’s input box, which is super simple.
Digital Guardian has specialized in helping organizations stop the theft of corporate data, like sensitive source code and intellectual property, since its inception. If you’re a customer, you should have the peace of mind that Digital Guardian’s data loss prevention solutions can help highlight and mitigate the risks associated with ChatGPT.
Digital Guardian can:
- Outright block: HTTP (unencrypted web traffic) and HTTPS (encrypted web traffic) going to https://chat.openai.com/ on endpoints (user's computers)
- Flag patterns: Monitor and block questions submitted to ChatGPT based on patterns such as: national insurance numbers, social security numbers, credit card number, sort codes, drivers’ licenses, ITAR (International Traffic in Arms Regulations) keywords, etc.
- Stop the exfiltration of classified data: Block copying and pasting of data tagged as classified by the eDLP agent or user to ChatGPT. i.e. tagged by government departments or enterprise classification like: Public, Official, Official-Sensitive, Secret or Top Secret
If a user attempts to copy and paste information from a classified file, Digital Guardian will prohibit the action and flag the attempt before the user has the opportunity to submit it to ChatGPT.
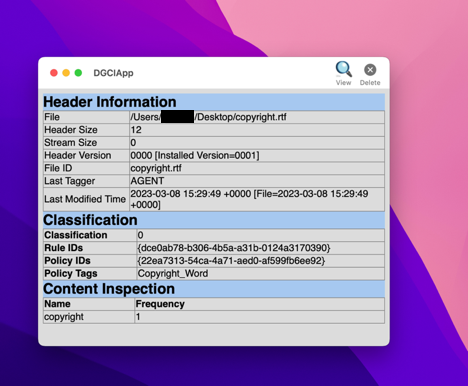
The above is a classified file along with tag.
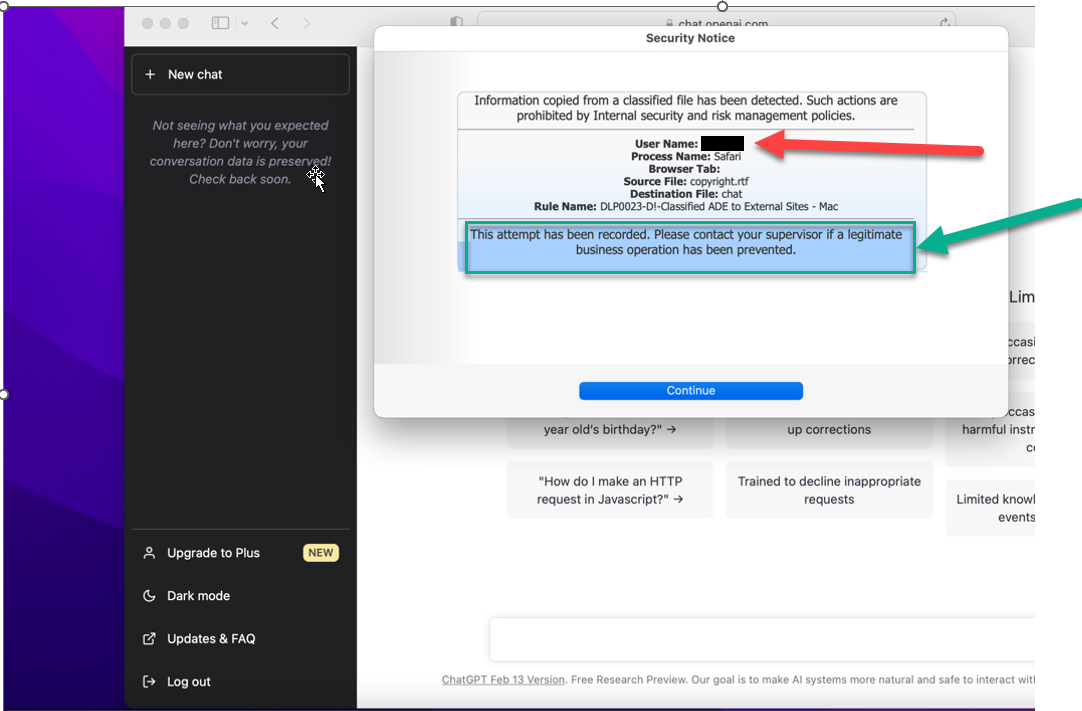
Once the contents of a classified file is copied/pasted into the question box, a prompt is thrown even without submitting the question.
Fortra’s Digital Guardian is a leader in data egress management helping organizations prevent the loss of its valued business data. ChatGPT, along with similar platforms such as Google Bard, are simply additional egress points covered by our leading solutions for data protection. We pride ourselves in our continued innovation, and responsiveness, to develop policies and rules preventing the exfiltration of data within the rapidly changing landscape of AI.


