What is Data Integrity?
Data integrity refers to the accuracy and consistency (validity) of data over its lifecycle. Compromised data, after all, is of little use to enterprises, not to mention the dangers presented by sensitive data loss. For this reason, maintaining data integrity is a core focus of many enterprise security solutions.
Data integrity can be compromised in several ways. Each time data is replicated or transferred, it should remain intact and unaltered between updates. Error checking methods and validation procedures are typically relied on to ensure the integrity of data that is transferred or reproduced without the intention of alteration.
Data Integrity as a Process and as a State
The term data integrity also leads to confusion because it may refer either to a state or a process. Data integrity as a state defines a data set that is both valid and accurate. On the other hand, data integrity as a process, describes measures used to ensure validity and accuracy of a data set or all data contained in a database or other construct. For instance, error checking and validation methods may be referred to as data integrity processes.
A Case for Data Integrity
Maintaining data integrity is important for several reasons. For one, data integrity ensures recoverability and searchability, traceability (to origin), and connectivity. Protecting the validity and accuracy of data also increases stability and performance while improving reusability and maintainability.
Data increasingly drives enterprise decision-making, but it must undergo a variety of changes and processes to go from raw form to formats more practical for identifying relationships and facilitating informed decisions. Therefore, data integrity is a top priority for modern enterprises.
Types of Data Integrity
Data integrity can be compromised in a variety of ways, making data integrity practices an essential component of effective enterprise security protocols. Data integrity may be compromised through:
- Human error, whether malicious or unintentional
- Transfer errors, including unintended alterations or data compromise during transfer from one device to another
- Bugs, viruses/malware, hacking, and other cyber threats
- Compromised hardware, such as a device or disk crash
- Physical compromise to devices
Since only some of these compromises may be adequately prevented through data security, the case for data backup and duplication becomes critical for ensuring data integrity. Other data integrity best practices include input validation to preclude the entering of invalid data, error detection/data validation to identify errors in data transmission, and security measures such as data loss prevention, access control, data encryption, and more.
Data Integrity for Databases
In the broad sense, data integrity is a term to understand the health and maintenance of any digital information. For many, the term is related to database management. For databases, there are four types of data integrity.
- Entity Integrity: In a database, there are columns, rows, and tables. In a primary key, these elements are to be as numerous as needed for the data to be accurate, yet no more than necessary. None of these elements should be the same and none of these elements should be null. For example, a database of employees should have primary key data of their name and a specific “employee number.”
- Referential Integrity: Foreign keys in a database is a second table that can refer to a primary key table within the database. Foreign keys relate data that could be shared or null. For instance, employees could share the same role or work in the same department.
- Domain Integrity: All categories and values in a database are set, including nulls (e.g., N/A). The domain integrity of a database refers to the common ways to input and read this data. For instance, if a database uses monetary values to include dollars and cents, three decimal places will not be allowed.
- User-Defined Integrity: There are sets of data, created by users, outside of entity, referential and domain integrity. If an employer creates a column to input corrective action of employees, this data would be classified as “user-defined.”
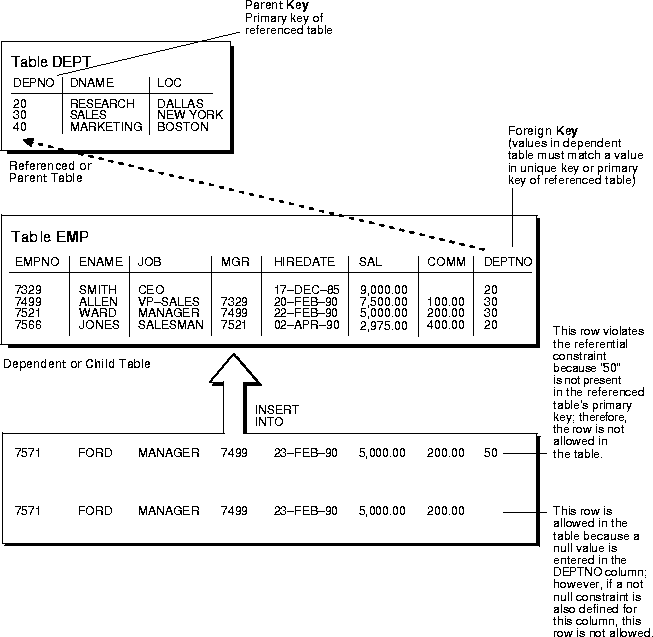
Image Source: Oracle
Data Integrity Vs. Data Security
Data integrity and data security are related terms, each playing an important role in the successful achievement of the other. Data security refers to the protection of data against unauthorized access or corruption and is necessary to ensure data integrity.
That said, data integrity is a desired result of data security, but the term data integrity refers only to the validity and accuracy of data rather than the act of protecting data. Data security, in other words, is one of several measures which can be employed to maintain data integrity. Whether it's a case of malicious intent or accidental compromise, data security plays an important role in maintaining data integrity.
For modern enterprises, data integrity is essential for the accuracy and efficiency of business processes as well as decision making. It’s also a central focus of many data security programs. Achieved through a variety of data protection methods, including backup and replication, database integrity constraints, validation processes, and other systems and protocols, data integrity is critical yet manageable for organizations today.
